Technical SuPPORT
Materials and Surface treatment
AlHotThe service life and load-bearing capacity of the gratings also depends on the materials used and surface protection.
1. Steel S235JR
The most commonly used structural steel for the production of gratings. Steel gratings are mainly used in the heavy, energy and automotive industries as footbridges, platforms, staircases and also as channel coverings.
2. Hot-dip galvanized according to EN ISO 1461
The highest quality surface protection of steel gratings. This involves immersing the gratings in hot zinc melt. An alloy of iron and zinc will thus be formed on the surface of the gratings. This metal layer forms a safe protection against the influence of wind, weather and mechanical loads.
Norm of zinc layers :
|
Parameters of materials |
Thickness Zn vrstvy |
|
Steel parts of thickness >= 1,5 < 3mm |
min. 55 μm |
|
Steel parts of thickness >= 3,5 < 6mm |
min. 70 μm |
|
Steel parts of thickness >= 6mm |
min. 85 μm |
3. Stainless steel 1.4301 (A2)
Gratings made of stainless steel are used in special operations of the food industry (breweries, dairies) and the chemical industry wherever there is a requirement for a high bearing capacity of the platform. The advantage of these gratings is several times higher resistance to corrosion compared to ordinary steel gratings.
4. Aluminum AlMg3
Aluminum gratings are mainly used as non-load-bearing elements of a steel structure, e.g. interior soffits or solar shading of building facades. Gratings are made to measure according to the customer’s request, mainly in the version – pressed gratings P.
5. Composite material
Gratings are made from a combination of fiberglass, resin and heat-cured dye. Gratings are light, non-conductive, color stable, highly resistant to corrosion. They are used in the food, oil, pharmaceutical and shipbuilding industries as platforms and floors of structures.
Production tolerancies

The gratings are made of supporting tapes that transfer the entire load to the grating, non-bearing and edging profiles. The basis for designing the grating structure is the size of the supporting tape, the size of the mesh, the shape and size of the non-bearing and edging bar.
Production tolerances of bearing and non-bearing gratings parameters according to RAL – GZ 638
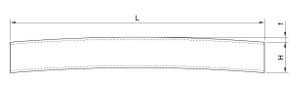
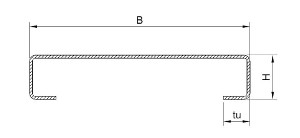
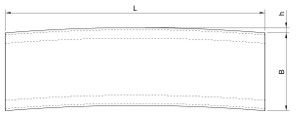
These production tolerances apply to all types of grids for the supporting belt max. 60×5 mm including and spacing of the supporting or spacing bars from 11 mm to 66 mm. The area of the gratings does not exceed 2 m².
L = +0mm; -4mm
B = +0mm; -4mm
i = +8mm; – 0mm
h = +8mm; – 0mm

Deflection of gratings:
omax = 1/200 bearing and non-bearing parameter of grating L if b > 600 mm, max. 8mm
for parameter L if b< 600 mm is omax = 3mm
Production tolerances of bearing and non-bearing gratings parameters according to RAL-GZ 639
Rules for designing and laying gratings
Adherence to the recommended distances when designing the gratings will ensure the correct design and simple assembly of the gratings on the beams of the steel structure, see pic. These pictures show the minimum gaps between the grating and the end of the steel beams. structures, the recommended distance of the gratings from the walls, from the pipe, from the main beam, if there is a minimum gap for storing the gratings in the frame, and also the recommended distances between the gratings during their assembly.
According to norm RAL – GZ 638 gratings are produced in minus tolerances, up to -4 mm. Therefore, it is possible to consider when designing the laying of gratings one behind the other on the drawing, the gap between the gratings is equal to 0. We recommend using the typified widths of the gratings on the largest possible scale, this will speed up the production of gratings and reduce their total price, see fig. proposal for laying SP gratings one behind the other.

Special Design
Form treatments
they are straight or circular cut-outs in gratings, when it is necessary to adapt the shape of the grating to the shape of the steel structure, e.g. during the passage of various technology through the gratings platforms.

Anti-slip stepping edge
is mainly used for stairs treads or gratings to prevent slipping.

KickPlate
strengthens and increases the edge of the grating and thus prevents objects from falling over the platform.

Raised border
it is used to achieve the same level of the upper edge of the grating with the profile of the steel structure.

Edging with L profile
is mainly used for shelf gratings, where the angle serves as a suspension of the grating between the profiles of the steel structure.

NormS
|
AGI Arbeitsblatt H10 |
Steel gratings in industry |
|
BGI 588 |
Steel gratings |
|
BGR 181 |
Floors in work areas with a risk of slipping |
|
DIN 1072 |
Loads for roads and bridges |
|
DIN 1055-3 |
Forklifts |
|
DIN 24531 |
Stairs treads from grating |
|
DIN 24532 |
Vertical solid steel ladders |
|
DIN 24537 |
Steel gratings |
|
DIN EN ISO 1461 |
Hot-dip galvanizing of steel products |
|
DIN EN ISO 14122 |
Safety of machinery (platforms and bridges, stairs) |
|
RAL – GZ 638 |
Tolerances for gratings |
|
RAL – GZ 639 |
Tolerances for profiles |